Phenotypes associated with this allele
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Tns1tm1Efu mutation
(0 available);
any
Tns1 mutation
(84 available)
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
 |
• valves show evidence of myxomatous degeneration as indicated by increased proteoglycan content and loss of natural matrix stratification
|
 |
• 9 month old mice show enlargement of posterior mitral leaflets
• slight leaflet displacement is observed consistent with larger leaflets, but no mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
| Find Mice |
Using the International Mouse Strain Resource (IMSR)
Mouse lines carrying:
Tns1tm1Efu mutation
(0 available);
any
Tns1 mutation
(84 available)
|
|
|
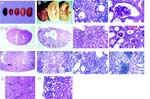
Kidney abnormalities in Tns1tm1Efu/Tns1tm1Efu mice
renal/urinary system
|
|
• pale kidney color suggests that fluid flow through the kidneys is compromised
|
|
|
• affected kidneys display signs of focal interstitial inflammatory infiltrates
|
|
|
• homozygotes exhibit a slow, progressive kidney degeneration with a variable onset time
• although ageing homozygotes generally display more severe kidney defects, some mice older than 6 months only show mild cystic defects
• in severe cases, the cortex and medulla are so compressed that mutant kidneys appear nearly empty
|
|
|
• mutant kidneys show variable cystic defects, ranging from extremely dilated cysts in the cortex and medulla in severely affected organs, to small cysts in the cortex in less affected organs
• most small cysts are derived from an expansion of the lumen of proximal tubules
• very small cysts can often be detected as early as 1-2 weeks after birth
• kidney cysts are prevalent even in homozygotes with normal blood analysis
|
|
|
• kidney cortex cysts range from extremely dilated to small, and often contain amorphous, noncellular materials, referred to as "casts"
• in cystic areas of the cortex, cell-matrix junctions are disrupted and tubule cells lack polarity; in contrast, noncystic areas display normal cell-matrix junctions
|
|
|
• mutant kidneys are often slightly larger than age-matched wild-type kidneys
|
|
|
• unlike wild-type kidneys which always display a dark reddish brown cortex, mutant kidneys show a less prominent color distinction between the cortex region and the lighter medulla
|
|
|
• many mutant glomeruli exhibit enlarged Bowman's spaces
|
|
|
• mutant glomeruli are surrounded by enlarged cuboidal epithelial cells with a prominent cytoplasm, rather than the normal thin flattened epithelia, barely visible in control glomeruli
• gross glomerular defects are often not observed until the adult stage
• however, neither fusions of foot processes nor separations of podocytes from their underlying basement membranes are observed
|
|
|
• in severely affected regions, signs of focal segmental glomerular sclerosis are observed
• in highly abnormal regions, the glomeruli are thickened and appear to contain extracellular depositions
|
|
|
• in many mutant kidneys, the renal pelvis opening is significantly enlarged
• an enlarged renal pelvis space can often be detected as early as 2 weeks after birth
|
|
|
• in severely affected kidney regions, microvilli are largely deteriorated, mitochondria are less organized and less abundant, and the basal membrane shows fewer invaginations; many cells show abnormalities in cell shape, and the epithelium appears to be less polarized
• in mildly affected areas, the cuboidal epithelium of proximal tubules is polarized and ultrastructurally normal, with numerous microvilli on the apical surface; fewer undulations of the basal membrane are occasionally observed
|
|
|
• in mildly affected kidneys, dilated tubules are concentrated in the kidney cortex
• most dilated tubules display residual microvilli, exclusive to the proximal tubules of the kidney
|
|
|
• kidney cortex cysts often contain amorphous, noncellular materials, referred to as "casts"
|
|
|
• mutant kidneys display a rough and granular surface, usually by ~4-8 weesk after birth
|
|
|
• homozygotes exhibit a slow, progressive kidney degeneration with a variable onset time
|
|
|
• mutant kidneys are uniformly pale, ranging from brown to light yellow, at all ages studied
|
|
|
• only 3 of 44 homozygotes (18 wk, 8 mo, and 9 mo of age) became visibly ill in a manner that might be consistent with renal failure
• all remaining homozygotes appeared clinically normal
|
reproductive system
 |
• in 14 matings of homozygous females and males, only nine produced offspring
|
|
|
• crosses between homozygous females and males yield an average litter size of only 3 pups, whereas crosses between homozygous males and either wild-type or heterozygous females produce normal litters, ranging from 7 to 9 pups
|
behavior/neurological
|
|
• homozygotes become progressively frail because of bilateral kidney abnormalities
• homozygotes with overt signs of weakness show signs of kidney failure and contain multiple large cysts in the proximal kidney tubules
|
immune system
|
|
• affected kidneys display signs of focal interstitial inflammatory infiltrates
|
cardiovascular system
|
N |
• homozygotes show no apparent defects in cardiac morphology and function
|
|
|
• pale kidney color suggests that fluid flow through the kidneys is compromised
|
cellular
|
|
• focal adhesions are present in apparently normal proximal tubules but are absent in cystic proximal tubular cells
|
growth/size/body
|
|
• mutant kidneys show variable cystic defects, ranging from extremely dilated cysts in the cortex and medulla in severely affected organs, to small cysts in the cortex in less affected organs
• most small cysts are derived from an expansion of the lumen of proximal tubules
• very small cysts can often be detected as early as 1-2 weeks after birth
• kidney cysts are prevalent even in homozygotes with normal blood analysis
|
|
|
• kidney cortex cysts range from extremely dilated to small, and often contain amorphous, noncellular materials, referred to as "casts"
• in cystic areas of the cortex, cell-matrix junctions are disrupted and tubule cells lack polarity; in contrast, noncystic areas display normal cell-matrix junctions
|
|
|
• mutant kidneys are often slightly larger than age-matched wild-type kidneys
|





 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools
