Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur
Transgene Detail
|
|
| Symbol: |
Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur |
| Name: |
transgene insertion 1, Mark E Gurney |
| MGI ID: |
MGI:2183719 |
| Synonyms: |
G1H, G93A, G93A+, G93A SOD1, G93A-SOD1, (G93A)Tg+, Gur1-G93A, hSOD1G93A, SOD1 G93A, SOD1G93A, SOD1 Tg, Tg(G93A-SOD1)1Gur, TgN(SOD1-G93A)1Gur, TgN[SOD1-G93A]1Gur, Tg(SOD1-G93A)1Gur |
| Transgene: |
Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur Location: unknown Genetic Position: Chr12, cytoband E
|
| Alliance: |
Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur page
|
|
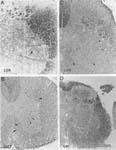
Presence of neurofilament spheroids in the spinal cord of an 82-day old Tg(SOD1)2Gur/0 mouse
Show the 5 phenotype image(s) involving this allele.
|
|
|
|
|
| Transgene Type: |
|
Transgenic (Humanized sequence, Inserted expressed sequence) |
| Mutation: |
|
Insertion
|
| |
|
Tg(SOD1*G93A)1Gur expresses
1 gene
Transgene expresses:
| Organism |
Expressed Gene |
Homolog in Mouse |
Note |
| human |
SOD1 (6647) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Mutation details: This transgenic subline (designated G1H in J:76718) is derived from the G1 parental transgenic line (originally described in J:32665). This line carries a 40% expansion in transgene copy number compared to the original G1 line (described in J:32665, in MGI as Tg(SOD1*G93A)2Gur). The transgene construct is composed of the human SOD1 gene carrying a glycine to alanine transition at position 93 (G93A). The G93A mutation does not alter the activity of the protein. This line carries a high copy number maps to Mus Chr12:97,165,800 (coordinates from MGSC ver 37, mm9).
(J:32665, J:76718)
|
|
|
View phenotypes and curated references for all genotypes (concatenated display).
|
|
|
|
|
| Mouse strains and cell lines
available from the International Mouse Strain Resource
(IMSR) |
| Carrying this Mutation: |
Mouse Strains: 4 strains available
Cell Lines: 0 lines available
|
|
This line, G1H, was derived from the original G1 line (now designated Tg(SOD1*G93A)2Gur) reported in J:32665. Transgenic mice on a background that involves C57BL/6 and SJL express high levels of the transgene with a 4-fold increase in SOD activity, and exhibit a phenotype similar to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in humans. Hemizygous transgenic mice become paralyzed in one or more limbs and have a life span of approximately 19-23 weeks. Paralysis is due to loss of motor neurons from the spinal cord. |
| Original: |
J:76718 Tu PH, et al., Transgenic mice carrying a human mutant superoxide dismutase transgene develop neuronal cytoskeletal pathology resembling human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):3155-60 |
| All: |
1163 reference(s) |
|
 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools





